By signing in or creating an account, you agree with Associated Broadcasting Company's Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy.


By signing in or creating an account, you agree with Associated Broadcasting Company's Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy.
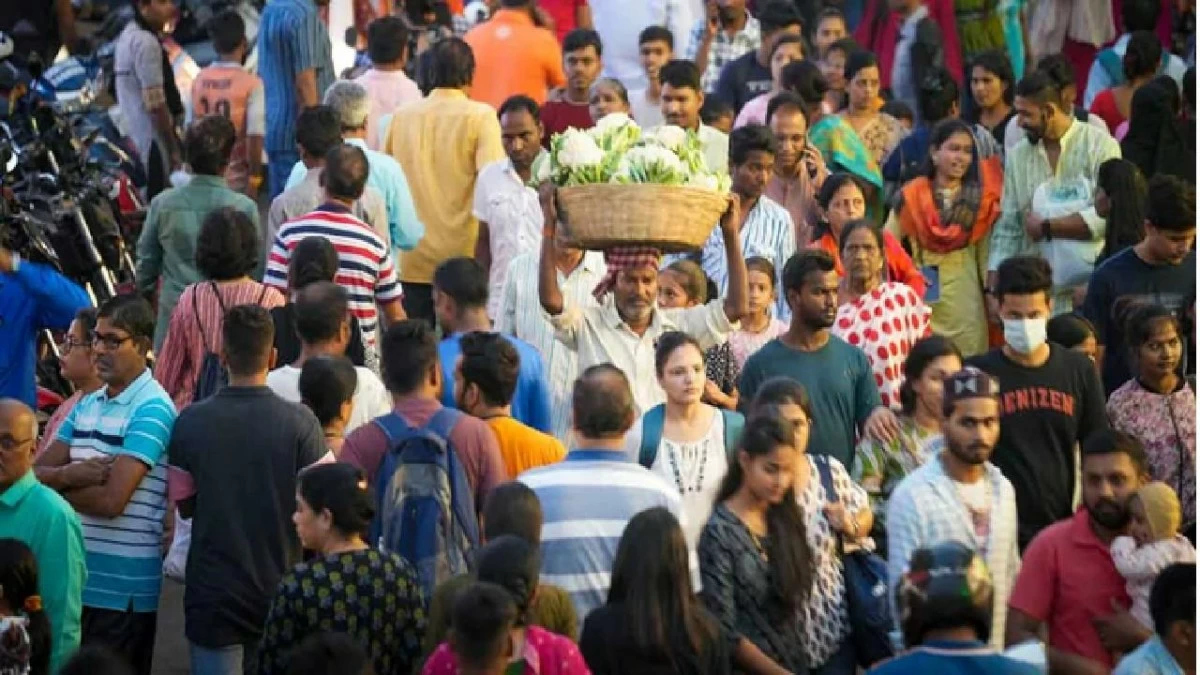

India's population today stands at around 1.4 billion. Despite various population control measures, the country continues to grapple with this critical question of population increase. Though there has been a slowdown in the population growth over the past decades, even a marginal increase adds up to millions of individuals every year. And in 2023, India surpassed China to become the world's most populous country with 1.428 billion people. According to UN estimates, India's population is likely to grow in the decades to come and may reach up to 1.7 billion by the 2060s, while China's continues to decline.
Let's us understand what are five major factors that drive India's population growth
High fertility rates in some regions: Though there has been a slight decline in the population growth across the country, there are still pockets of areas where the population growth is said to be a bit higher. Some of these regions include Uttar Pradesh, Bihar and Jharkhand. Compared to their southern counterparts, these regions continue to exhibit higher total fertility rates. Some of the reasons attributed to the higher birth rates in these regions are low level of education, limited access to healthcare, and patriarchal norms adhering to large families. Cultural and religious beliefs also play a part in it especially in rural belts. A desire for male children due to societal consideration also contributes to higher birth rates.
Limited access to family planning measures: For decades, India has successfully implemented family planning programmes across various parts of the country. However, there are areas where gaps remain and the concept of family planning is yet to be adopted. Limited access to contraceptives, social stigma greatly hinder the family planning programme and its adoption.
Declining Mortality Rates and Increased Life Expectancy: With in improvement in health infrastructure, sanitation and disease control there has been a decline in mortality rate especially infant and maternal mortality in the country. While increase in life expectancy at the same time has also contributed to population growth.
Poverty and lack of economic opportunities: In rural areas where there is widespread poverty and lack of employment opportunities, more members in the family are considered as an economic asset to support the family. Limited access to education and economic opportunities, especially women, also exacerbate the increase in birth rate. To manage the issue of poverty, there is a greater need to empower women members in the family through promotion of education and economic opportunities which in turn helps in population control.
Early marriage and teenage pregnancies: Another problem in the rural set up in India is the early marriages of girls and subsequent teen pregnancies. The trend is worrisome especially in marginalised communities in the country. The teenage pregnancies often result due to lack of sexual and reproductive healthcare education in the early marriages and thus leading to higher birth rate. This trend not only endangers the health and well being of the woman and the child, but also contributes to population growth.